This post continues our new series, The Smart Scholar, which explores the attributes and qualities that make a successful academic applicant.
As the academic year is coming to a close, the summer is an excellent time to reflect and evaluate where you are on your journey to seeking your next academic position. For some this means engaging in the beginning development of your dissertation proposal, data collection, or editing of your dissertation/thesis. For others, this time is valuable for putting together your job materials (such as your CV, cover letter, teaching philosophy, etc.) for the upcoming job season. Regardless of the everyday tasks at hand, now is an excellent opportunity to put a plan in action so that the job of your dreams can become your reality.
Given this context, below are two practices, especially relevant to those that are underrepresented in higher education, that can be developed during the summer as you prepare to land your dream job.
Cultivate your village of mentors
There is the African proverb that says, “It takes a village to raise a child.” I would argue that to land a position in higher education it takes at least a village. So how do you develop relationships that will help you be successful?
As you think about this, consider the following questions: who are the people that affirm me as a scholar and/or can help me navigate the job market to land my position? I propose these questions as I believe it is critical that you develop a deep bench of mentors—one person will never be able to meet all of your needs or criteria for success. Thus, you should take the time to search for people who:
- Can support your job application materials
- Can speak in rooms on your behalf
- Push you to submit the application
- Will be in and stay in your corner during the best of times and the worst of times
Moreover, success in the job market, for better or worse, often comes down to who you know and who knows you. So taking the time to cultivate your village could make the difference in landing your next position.
One such venue to develop this scholarly village is a group called R. A. C. E. (Research, Advocacy, Collaboration, Empowerment) Mentoring, which was co-founded by Drs. Donna Y. Ford, Michelle Trotman Scott, and Malik S. Henfield. R.A.C.E. Mentoring (also referred to by group members as RM) is a virtual Facebook group of over 700 members that provides support, mentoring, and professional development to faculty and graduate students of color to increase their representation in higher education.
In addition to the virtual networking, a summer conference will be held at Vanderbilt University July 13-15, 2018 which would be an excellent opportunity to connect with scholars across the country who can become part of your village.
Assess the needs of the job market against your current skill-set and fill in the gaps
As graduate students, we engage in training that prepares us to be researchers. However, depending on your particular institution you may have had (or not had) certain experiences to develop skill-sets needed to land your next academic position.
- To account for this possible gap, you should take time to assess, “What are the requirements for someone to land the job I’m looking to go after?”
- Once you do this assessment, the next step is for you to reflect and determine if you met all of the necessary skill-sets to make yourself a viable candidate. To make this determination, work with your scholarly village as they will have an understanding about the skills you may need to secure your next position.
- Lastly, if for some reason you need a certain expertise that you do not currently have, develop a plan to get that experience. For instance, if positions in your field require experience securing grants and you did not have the opportunity to work on a grant during your scholarly training, it would be beneficial to engage in grant writing training and collaborate with others who have been successful grant writers so that you can learn the craft. While gaining a new skill set like this won’t happen overnight, taking the time to develop it will pay dividends when you seek your ideal academic position.
With the increasing use of online learning platforms, gaining some of these experiences and skill-sets can occur from the comfort of your home. Moreover, this would be an excellent time to work with your village of mentors to help solidify your plan.
As you develop your summer plans, I look forward to hearing about how you have landed your dream position this upcoming year. And if you need a member in your village for support, count me in! I’d love to hear your progress via Twitter (@ramongoings).
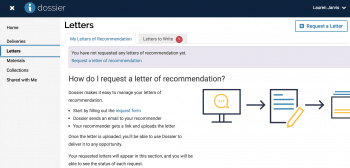
Interfolio’s Dossier enables scholars to collect, curate, polish and send out their materials at all stages throughout their academic professional path. Learn more about Dossier here.
Author Bio: Dr. Ramon B. Goings is an assistant professor of educational leadership at Loyola University Maryland. His research examines gifted/high-achieving Black male academic success PreK-PhD, diversifying the teacher and school leader workforce, and the student experience and contributions of historically Black colleges and universities to the higher education landscape. As a writing coach and editor, Dr. Goings enjoys supporting the scholarly development of doctoral students and professors in higher education. For more information about Dr. Goings, please visit his website www.ramongoings.com and follow him on twitter (@ramongoings).